Lasers have revolutionized the modern world. Since their invention in the 1960s, lasers—short for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation”—have found applications in nearly every sector of science, technology, medicine, and industry. Understanding the applications of laser helps us appreciate how this focused beam of coherent light has transformed our lives—from precision surgeries to data transmission.
In this article, we’ll explore the applications of laser in various fields including medicine, manufacturing, communication, military, and everyday technology.
Fundamental Properties That Enable Laser Applications
Before delving into the applications of laser, it’s essential to understand the properties that make lasers unique:
-
Monochromaticity – Lasers emit light of a single wavelength.
-
Coherence – Laser waves are in phase, allowing precise energy focus.
-
Directionality – Laser beams are highly directional and don’t spread like conventional light.
-
High Intensity – Concentrated light enables cutting and drilling.
These properties allow lasers to be used in a wide range of settings, from delicate eye surgeries to industrial metal cutting.
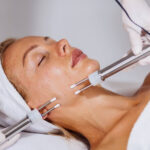
Medical Applications of Laser
One of the most profound applications of laser is in the field of medicine. Lasers have become indispensable tools for both diagnosis and treatment.
1. Laser Eye Surgery
-
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) reshapes the cornea to correct refractive errors such as myopia and hyperopia.
-
It is a painless, fast, and highly accurate method, improving vision without the need for glasses or contact lenses.
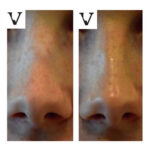
2. Dermatological Treatments
-
Used for tattoo removal, skin resurfacing, acne scar reduction, and wrinkle treatments.
-
Fractional CO₂ lasers promote collagen formation, improving skin texture.
3. Cancer Treatment
-
In photodynamic therapy, lasers activate photosensitive drugs to kill cancerous cells.
-
Laser ablation removes tumors with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
4. Dental Procedures
-
Lasers offer painless treatment for cavities, gum diseases, and teeth whitening.
-
Reduce the need for anesthesia and minimize bleeding.
Industrial Applications of Laser
In manufacturing and engineering, the applications of laser have improved speed, precision, and automation capabilities.
1. Laser Cutting and Drilling
-
High-powered lasers cut through metals, plastics, and ceramics with extreme precision.
-
Used in automotive and aerospace industries for detailed component fabrication.
2. Laser Welding
-
Ensures strong and clean joints in metallic parts.
-
Ideal for delicate or hard-to-reach places where traditional welding fails.
3. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
-
Laser sintering fuses powdered materials into 3D shapes, used for prototyping and custom parts.
4. Surface Treatment
-
Laser hardening improves wear resistance in tools and machinery.
-
Used for engraving, marking barcodes, and serial numbers on products.
Applications of Laser in Communication
Lasers form the backbone of high-speed communication systems, especially in the era of digital and optical data transfer.
1. Fiber Optic Communication
-
Lasers transmit data as light pulses through optical fibers at extremely high speeds and over long distances.
-
Forms the core of internet and telephone networks.
2. Free Space Optical Communication
-
Laser beams are used to send data wirelessly between satellites or buildings when fiber optics are not feasible.
3. Li-Fi Technology
-
A new frontier in wireless communication where LED and laser light transmit data faster than traditional Wi-Fi.
Scientific and Research Applications of Laser
In laboratories and research centers, lasers are tools for exploring the fundamental laws of physics and chemistry.
1. Spectroscopy
-
Lasers analyze the composition of materials by studying the interaction of light with matter.
-
Used in environmental monitoring, drug testing, and forensic science.
2. Holography
-
Lasers create three-dimensional images by recording and reconstructing light fields.
-
Applied in medical imaging, security, and entertainment.
3. Nuclear Fusion Research
-
High-powered lasers initiate fusion reactions in experimental reactors, paving the way for clean energy solutions.
4. Optical Tweezers
-
Laser beams trap and manipulate microscopic particles or cells without physical contact.
-
Valuable in biological and genetic research.
Military and Defense Applications of Laser
Laser technology also plays a pivotal role in enhancing national defense and military capabilities.
1. Target Designation and Rangefinding
-
Lasers help soldiers and aircraft accurately aim and measure distances to targets.
-
Improve weapon precision and reduce collateral damage.
2. Directed Energy Weapons
-
Experimental laser weapons can disable drones, missiles, or vehicles without ammunition.
-
Offer silent and cost-effective defense solutions.
3. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
-
Used for 3D mapping of terrain, object detection, and surveillance.
-
Increasingly employed in autonomous vehicles and robotics.
Consumer and Entertainment Applications of Laser
Many don’t realize that the applications of laser also touch our daily lives in ways we often overlook.
1. Barcode Scanners
-
Found in supermarkets, these use laser beams to read product barcodes quickly and accurately.
2. Optical Disc Reading
-
CD, DVD, and Blu-ray players use low-powered lasers to read data stored on discs.
3. Laser Printers
-
Employ lasers to project images or text onto a drum, which is then printed on paper.
4. Laser Light Shows
-
Widely used in concerts and public displays for visual effects.
Environmental and Agricultural Applications of Laser
Emerging applications of laser in environment and agriculture contribute to sustainable practices.
1. Precision Agriculture
-
LIDAR and laser-based sensors monitor crop health, soil conditions, and irrigation needs.
-
Increase yields and reduce waste.
2. Pollution Monitoring
-
Lasers detect greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants in real-time.
3. Forest Mapping
-
Used for detailed forest structure analysis, biodiversity studies, and fire risk assessments.
Emerging Technologies Using Laser Applications
As laser technology continues to evolve, new possibilities emerge across disciplines.
1. Quantum Computing
-
Lasers control quantum bits (qubits) in highly sensitive computing systems that promise unprecedented processing power.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
-
Laser-based LIDAR systems help in real-time navigation and obstacle detection.
3. Space Exploration
-
NASA and other space agencies use lasers for satellite communication, asteroid mapping, and landing missions.
Limitations and Safety Concerns
Despite the vast applications of laser, safety and limitations must be addressed.
-
Eye and Skin Hazards: Direct exposure to laser beams can damage eyes and skin.
-
High Cost: Industrial and medical laser systems are expensive to install and maintain.
-
Power Limitations: Certain applications require high energy which can limit portable use.
Proper regulations, training, and safety measures are essential in environments where lasers are used.
Conclusion: Why Applications of Laser Matter
The widespread applications of laser across sectors underscore the transformative impact of this technology. From saving lives in surgeries to powering global communication, lasers are foundational tools in the modern era. As new innovations continue to push boundaries, laser technology will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future.
By understanding the vast and varied applications of laser, we not only appreciate their utility but also recognize the need for responsible and innovative development.